Conveyor Belt Manufacturers Industry Report: Market Growth, Automation & Sustainability Trends
Conveyor belts are the backbone of material handling in the present day. Conveyor belts are used to transport raw materials and the finished products on a factory-wide basis in the mines, factories, airports, warehouses and food-processing lines. The industry will be informed by an average yet consistent growth in the market over the next ten years, as well as technology and sustainability shifts that are altering the expectations of buyers of conveyor belt manufacturers. We discuss in this blog that gathers together conveyor belt market size estimates, growth opportunities and the tangible trends (automation, IoT, materials, sustainability and more) which are transforming the industry worldwide and in India.

1. Rapid market overview (global and India)
International market (recent estimations). Various market research studies estimate the conveyor-belt market across the world to be in the low-to-mid single-digit billions (USD). As an example, one of the analyst groups estimates the market to be passed by mid-2024 of around USD 5.7 billion with consistent growth over the coming years.
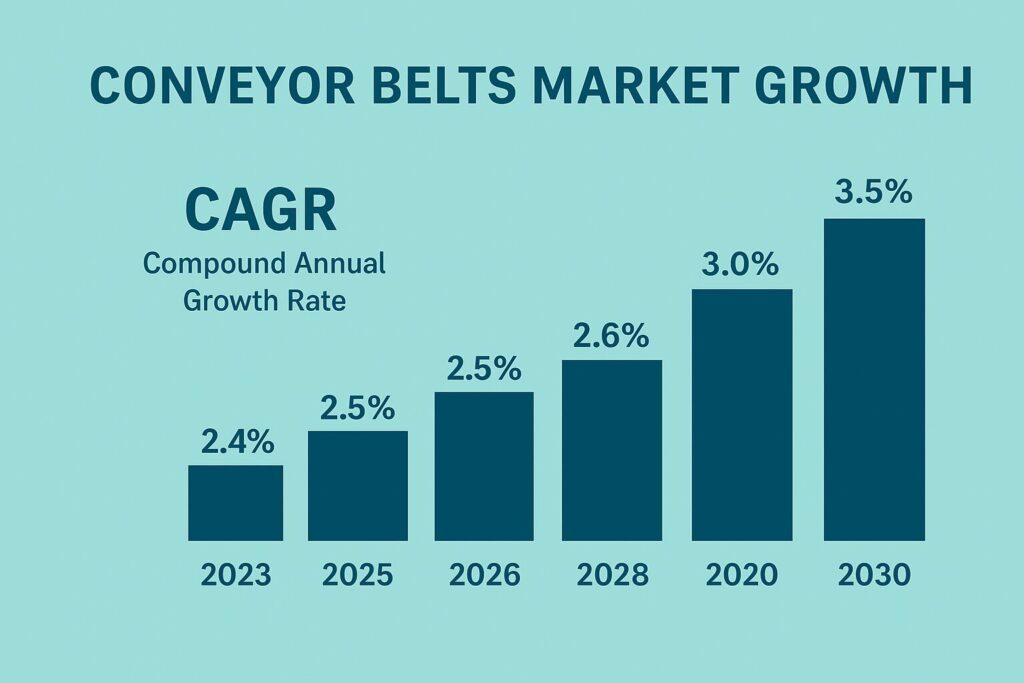
Other respectable reports share those order-of-magnitude figures and alone appear to project further growth (CAGR of about 3-4.5 per cent based on forecast horizon) due to increased activity in the mining, automation of manufacturing, logistics and food and beverage industries.
India market (recent estimates). India is a significant regional market – an analysis of the India conveyor belt market in 2024 estimated the market at approximately USD 557 million (2024) and is expected to grow into the late 2020s and early 2030s (CAGR of approximately 4-5). Infrastructure development, modernisation of mining and domestic production are mentioned as the sources of growth in India.
Bottom line: the conveyor-belt market is not a sizeable semiconductor or cloud software leader, but is large, long-lasting and growing steadily, particularly in the intersections of heavy industry, warehouse upgrades and automation investments.
2. The reason the market is expanding - major demand drivers
- Automation of industries and reshoring of manufacturing. When manufacturers are updating production lines or reshoring their operations, they invest in modern conveyor systems that are connected to automated material handling systems. This drives up the sales of new belts (and replacements).
- Modernisation of e-commerce and logistics. Parcel sortation centres and warehouses need high-throughput, modular conveyor systems; warehouses and upgrades are repeat business to the belt manufacturers.
- Demand for mining and bulk materials. The demand for heavy-duty belts and engineered solutions is driven by the mining capex cycles and the worldwide need for minerals and aggregates.
- Food, pharmaceuticals (hygienic, high-speed conveyor). Tight hygiene and traceability standards encourage the use of PU/TPE belts and modular solutions, and new product lines of higher margins appear.
- Replacement & aftermarket. Conveyor belts are wearable; the replacement cycles, as well as services (splicing, inspection, predictive maintenance) are permanent revenue streams that do not depend on the installation of new systems.
3. Best trends changing the conveyor belt manufacturing
A. Smart/connected belts: IoT, sensors and predictive maintenance
Conveyor systems are becoming progressively equipped with vibration sensors, belt-health devices, edge sensors and cloud analytics. Predictive maintenance minimises unexpected downtime and overall cost of ownership – a key marketing point to companies with large industry clients and logistics operators. According to market reports, IoT and predictive maintenance is one of the key trends that allow building a smart conveyor system.
The implication of this to manufacturers: offer systems as a service (monitoring, alerts, spare parts plans), collaborate with IIoT vendors and design belts with sensor integration locations.
B. Automation and modular (Industry 4.0 integration)
Modular conveyor belts (easy to reconfigure), servo-controlled lines, and built-in sortation modules are beginning to dominate the new warehouses and flexible production lines. It is particularly being adopted where the SKU complexity and its regular change of direction require flexibility.
pangindustrial.com
Opportunity: those manufacturers offering modular and plug-and-play belts and controls are enjoying bigger margins and repeat retrofit endeavours.
C. Innovation in materials – PU, TPE, covered fabrics, lighter constructions
Food, pharma and light manufacturing. Traditional rubber belts are still used in heavy material handling, although thermoplastic (PU/TPE) belts, lightweight polymers and coated fabrics are increasing in use due to their hygiene, abrasion resistance and reduced energy use. Such materials also allow faster and less noisy operation.
Implication to manufacturing: R&D on new compound formulations, collaborations with polymer suppliers and investments in extrusion/molding lines.
D. Sustainability and circularity
Sustainability is not a choice anymore. Buyers seek belts that require less energy in their life cycles, are recyclable, and that use processes that are greener to the environment. These can be longer-lasting belts (which would not need replacement), recyclable belt formulas and better energy efficiency in production. Sustainability also assists OEM customers in achieving their personal ESG targets.
Business case: the manufacturers can turn sustainability investment into differentiation, eco-labels, extend warranty, and take-back/recycling.
E. Modularization, light maintenance design and safety
Quick-belt replacement playbooks, standardized splicing, less hazardous materials, and workplace features that lower worker intervention are being demanded — particularly in high-speed logistics and food processing. These minimize regulatory compliance risk and downtime.
4. Manufacturers and service providers' opportunities

- Aftermarket/services – Remote monitoring subscriptions, predictive maintenance contracts, urgent splicing/ repair services and a spare-parts stock program produce recurring revenues.
- Warehouse products upgrades include modular belt, sortation and robot integration, and retrofit kits on older systems.
- High hygienic product lines — PU/TPE belts that are food/pharma certified in terms of traceability and cleanability.
- Sustainable lines/ recycling programs – develop closed-loop products (take-back, refurbish, recycle) to attract large customers with an ESG focus.
- local production + express delivery to India and other emerging markets – short lead times, local splicing knowledge, and localization can overtake imports on even project-sensitive projects.
5. India-specific (market environment and domestic opportunity) notes
- Infrastructure development, logistics and warehousing development (e-commerce and 3PL development), some states have mining activity, and there is an incentive to move towards Make-in-India modernization of factories, are all growth drivers in India. These take part in fresh installs and replacement demand.
- Sensitivity to price and customization: Indian customers tend to compromise between cost and lifetime; companies providing strong warranty, local splicing/service team and on-site training get big bids.
- Opportunity to domestic players: Indian manufacturers have two competitive levers in opportunity which are import substitution of standard belts and quick response to the aftermarket. Premium segments can be unlocked by investing in the Internet of Things and hygienic product lines.
6. Challenges & risks to watch
- Fluctuations in prices of raw materials. Prices of rubber and polymer feedstock are also influenced by the oil and commodity market, which narrows margins. Manufacturers have to juggle between inventory and hedging and pass-through pricing.
- The presence of large multinationals as suppliers. Large international players play the game of technology and size; domestic companies have to differentiate their offering on service, specialization and lead times.
- Standards & certifications. Food/pharma and certain mining industries need rigid certifications and documentation; it is expensive, yet mandatory to enter the market.
- Integration complexity. Buyers are demanding conveyors integrating WMS, PLCs and robotics- this is pushing control-system savvy.
7. Practical recommendations (to manufacturers and buyers)
In the case of conveyor belt manufacturers
- Invest in IIoT or collaborate with reputable IIoT companies to provide monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Grow after-sales services (quick repairs, splicing crews, subscription management). These are stabilizing revenue by the cycles.
- Make PU/TPE lines and modular belt products in hygienic, used in logistics and food applications; these are more profitable and quicker to expand.
- Introduce sustainability programs (longer life compounds, take-back programs) and ensure environmental claims can be verified.
In the case of buyers (plant managers, procurement)
- Consider the total cost of ownership and not only the purchase price – downtime risk, energy consumption, and maintenance should be part of the supplier assessment.
- Designate sensors and integration points in the RFPs to facilitate prospective predictive maintenance.
- Request suppliers to provide commitments and SLAs (on-site splicing) of spare parts and service response times. Increased local capability can outmatch a cheaper, remote supplier.
8. The proximate future (the future of 2028 - 2035)
- Slow and consistent market growth (low single-digit worldwide CAGR), and areas of greater improvement (e.g., logistics, food/pharma, modular systems).
- Greater use of smart belts and predictive maintenance – remote monitoring is a common practice in bigger installations.
- The material transformation impact and sustainability will form high-speed segments and new business models (recycling, refurbishment).
The conveyor-belt business provides long-term, stable opportunities as opposed to short-term, explosive growth. To manufacturers, the future of increased value is in intelligent, service-commodity, material development (PU/TPE and modular forms) and verifiable sustainability solutions. To buyers, the integration preparation, TCO measures, and service SLAs will safeguard operations and lower life-cycle equipment expenses.